Lazer Magnet Therapy
laser magnetic therapy apparatus: alleviate various joint inflammations
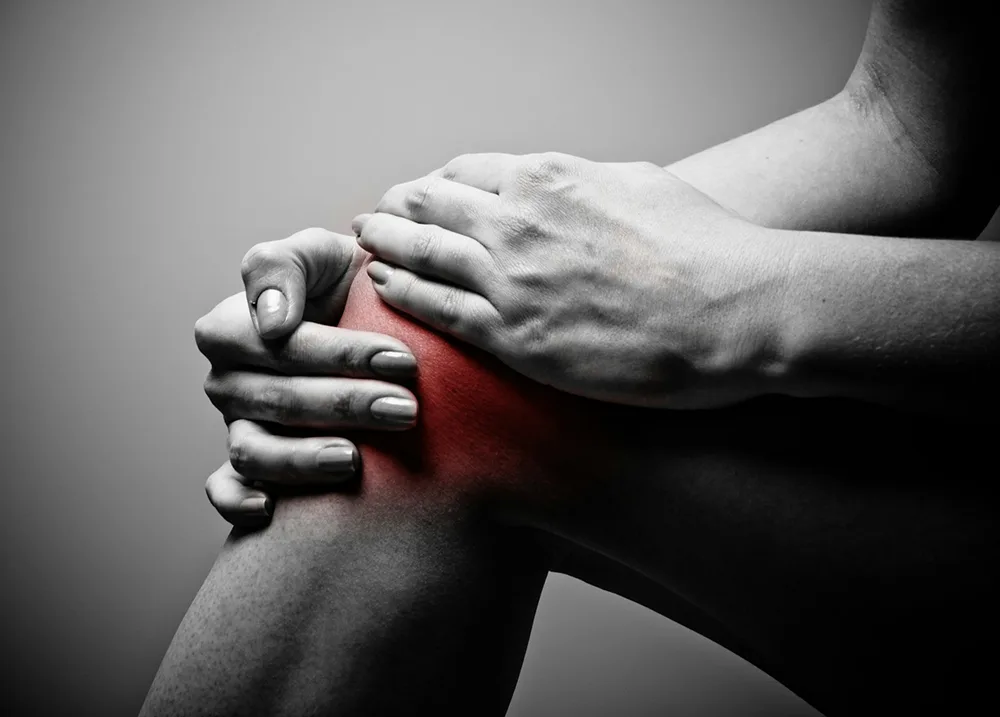
The mechanism by which laser magnetic therapy apparatus alleviates joint inflammation lies in the synergistic effect of laser and magnetic field, which improves the local inflammatory environment and promotes tissue repair from physical and physiological perspectives, thereby reducing symptoms such as pain and swelling. Specifically, its action pathways mainly include the following aspects:
I. Anti-inflammatory and repair effects of laser
- Inhibiting the release of inflammatory factors
Low-intensity lasers with specific wavelengths (such as 650nm, 808nm, etc.) can penetrate the skin to reach deep joint tissues. Through photobiomodulation, they reduce the accumulation of local inflammatory cells (such as macrophages and leukocytes) and inhibit the synthesis and release of inflammatory factors (such as tumor necrosis factor TNF-α, interleukin IL-1β, etc.), thereby alleviating the inflammatory response at the source. - Promoting local blood circulation
After the laser energy is absorbed by tissues, it can dilate the capillaries around the joints, increase local blood flow and oxygen supply, accelerate the excretion of inflammatory metabolites (such as lactic acid, histamine, etc.), and relieve swelling and pain caused by the accumulation of metabolites. - Accelerating tissue repair
Laser energy can activate the activity of cell mitochondria, promote the synthesis of ATP (cellular energy substance), enhance the proliferation and activity of fibroblasts, chondrocytes, etc., and accelerate the repair of damaged joint synovium, cartilage, and surrounding soft tissues, thereby improving joint function.
II. Analgesic and regulatory effects of magnetic field
- Alleviating pain signal transmission
When a constant or alternating magnetic field acts on the joint area, it can affect the excitability of nerve endings, reduce the speed and intensity of pain signals transmitted to the central nervous system, and at the same time promote the release of endorphins (the body’s natural analgesic substances), thereby reducing pain. - Regulating local ion balance
Magnetic field can change the distribution and movement state of ions (such as calcium ions, potassium ions) in tissues, stabilize the cell membrane potential, reduce the release of inflammatory mediators, and alleviate tissue edema to relieve joint swelling. - Improving the local microenvironment
Magnetic field can promote local blood circulation and lymphatic return, enhance tissue metabolism, help clear inflammatory products, and create a favorable environment for the repair of damaged tissues.
III. Synergistic effect enhances efficacy
The combined application of laser and magnetic field can work synergistically from multiple dimensions of “anti-inflammation, analgesia, and repair”: laser directly acts on the cellular level to inhibit inflammation and accelerate repair, while magnetic field enhances analgesic and detumescent effects through nerve regulation and microenvironment improvement. Their combination can more comprehensively relieve symptoms such as redness, swelling, heat, and pain caused by joint inflammation, and is especially suitable for adjuvant treatment of chronic joint inflammations such as degenerative arthritis (osteoarthritis), synovitis, and rheumatoid arthritis.
It should be noted that laser magnetic therapy apparatus is a physical therapy device, and its effect varies from person to person. It is mainly used to assist in relieving symptoms and cannot completely replace drugs or other targeted treatments. Specific use should be carried out under professional guidance.
